Top Papers of the week
1.) Tracing the thoughts of a large language model ( blog | paper1 | paper2 )
Anthropic's research on the Claude language model reveals key insights:
Multilingual Ability: Claude uses a shared conceptual space across languages, enabling knowledge transfer and suggesting a universal "language of thought."
Poetry: It plans ahead for rhyming, showing foresight and flexibility.
Mental Math: Claude combines approximation and precise calculation to solve problems, reflecting complex internal strategies.
Reasoning: It performs multi-step reasoning by integrating facts, demonstrating adaptability.
Hallucinations: Claude avoids guessing to reduce hallucinations but can still falter in some cases.
Jailbreaks: Specific prompts can bypass safety mechanisms, exploiting coherence-safety conflicts.
2.) Synthetic Video Enhances Physical Fidelity in Video Synthesis ( webpage | paper )
We explore enhancing video generation models using physics-consistent synthetic videos from computer graphics. These videos maintain 3D consistency and improve model fidelity by reducing artifacts. Our method curates synthetic data and transfers its realism, boosting physical consistency across tasks. While not fully understanding physics, this work shows synthetic videos can enhance physical fidelity in video synthesis.
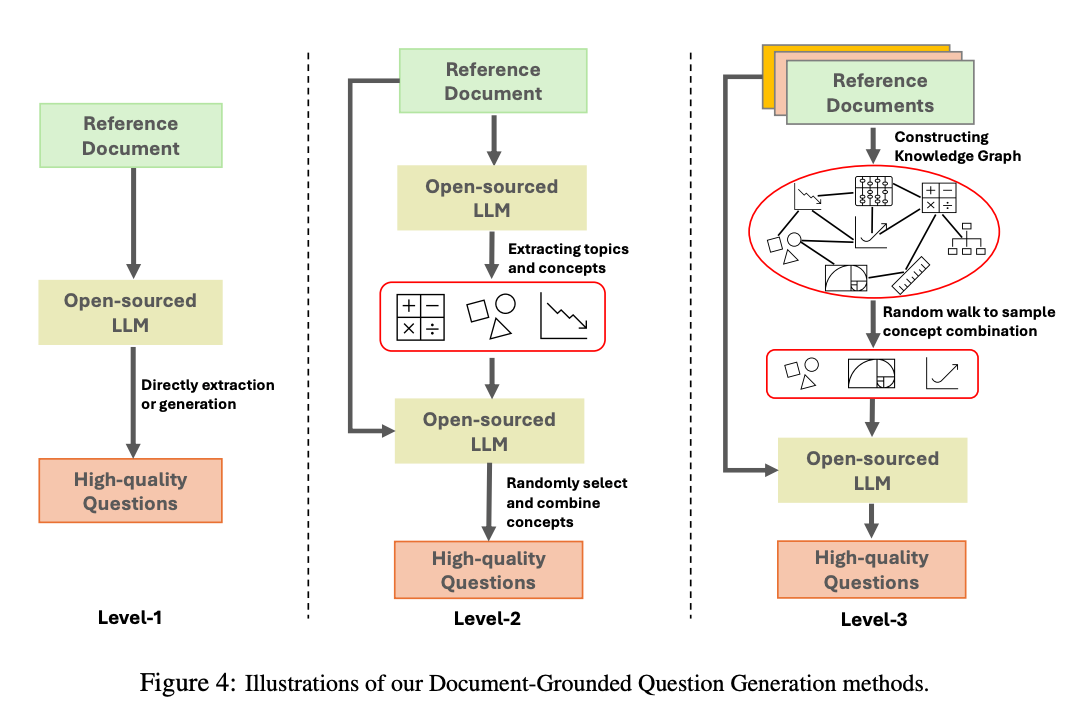
3.) Exploring Data Scaling Trends and Effects in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback ( paper )
RLHF is essential for aligning large language models with human preferences, but prompt-data construction has been neglected. This paper explores data-driven bottlenecks in RLHF performance scaling, focusing on reward hacking and reduced response diversity. We propose a hybrid reward system combining RTV and GenRM to counter reward hacking and introduce Pre-PPO to maintain response diversity and boost learning efficiency. Prioritizing math and coding tasks early in training also significantly improves performance. Experiments on two model sizes show that RTV is most resistant to reward hacking, followed by GenRM with ground truth and then GenRM with SFT Best-of-N responses. Our methods capture task-specific nuances quickly, enhancing overall RLHF performance. This work highlights the importance of careful data construction and provides practical solutions to overcome performance barriers in RLHF.
4.) Gemini Robotics: Bringing AI into the Physical World ( paper )
Recent advancements in multimodal models have shown promise in digital domains, but translating these capabilities to physical robots remains challenging. This report introduces Gemini Robotics, a new family of AI models built on Gemini 2.0, specifically designed for robotics. Gemini Robotics is a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that can directly control robots, performing complex manipulation tasks with smooth, reactive movements. It is robust to variations in objects and environments and can follow diverse instructions. With fine-tuning, it can tackle long-horizon tasks, learn new tasks from few demonstrations, and adapt to novel robot embodiments. This is enabled by Gemini Robotics-ER, an extended model that enhances spatial and temporal reasoning for robotics tasks such as object detection, trajectory prediction, and 3D bounding box predictions. The Gemini Robotics family represents a significant step towards general-purpose robots, addressing safety considerations and unlocking AI's potential in the physical world.
5.) Qwen2.5-Omni Technical Report( paper )
We present Qwen2.5-Omni, an end-to-end multimodal model handling text, images, audio, and video inputs while generating text and speech responses in a streaming manner. It uses block-wise processing for audio and visual inputs, synchronized via TMRoPE. The Thinker-Talker architecture separates text (Thinker) and speech (Talker) generation to prevent interference, with Talker using sliding-window DiT for low-latency audio decoding. Qwen2.5-Omni outperforms Qwen2-Audio, matches Qwen2.5-VL, and sets new benchmarks on Omni-Bench, excelling in speech instruction following, robustness, and naturalness.
6.) Scaling Laws of Synthetic Data for Language Models ( paper )
Large language models (LLMs) rely on high-quality web data, but this resource is depleting. Synthetic data offers a solution, though its scalability remains uncertain. We propose SynthLLM, a framework that creates high-quality synthetic datasets by recombining concepts from pre-training corpora. Key findings include: (1) SynthLLM follows scaling laws reliably, (2) performance plateaus at 300B tokens, and (3) larger models need fewer tokens to optimize. SynthLLM outperforms existing methods, proving synthetic data as a scalable alternative for advancing LLM performance.
7.) GAIA-2: Pushing the Boundaries of Video Generative Models for Safer Assisted and Automated Driving( blog | paper )
Generative models enable environment simulation but lack key features for autonomous driving, like multi-agent interactions and multi-camera consistency. We present GAIA-2, a latent diffusion model that generates controllable, high-resolution, spatiotemporally consistent videos across diverse driving environments. GAIA-2 integrates structured inputs and latent embeddings to simulate complex, scalable driving scenarios, advancing autonomous system development.
8.) ChatAnyone: Stylized Real-time Portrait Video Generation with Hierarchical Motion Diffusion Model( webpage | paper )
Real-time interactive video-chat portraits are advancing but struggle with synchronized body motions and fine control over expressions. We propose a framework for stylized video generation, extending from talking heads to upper-body interaction. Using hierarchical motion diffusion and explicit hand control, our method generates expressive, synchronized videos at 512×768 resolution, 30fps, enabling real-time, natural video chats with rich gestures and realism.
9.) What, How, Where, and How Well? A Survey on Test-Time Scaling in Large Language Models ( paper )
As pretraining-era scaling wanes, test-time scaling (TTS) has gained focus, enhancing LLMs' problem-solving in tasks like math, coding, and open-ended Q&A. This survey introduces a unified framework across four TTS dimensions: what, how, where, and how well to scale. We review methods, applications, and challenges, offering deployment guidelines and future directions for further scaling and broader generalization.
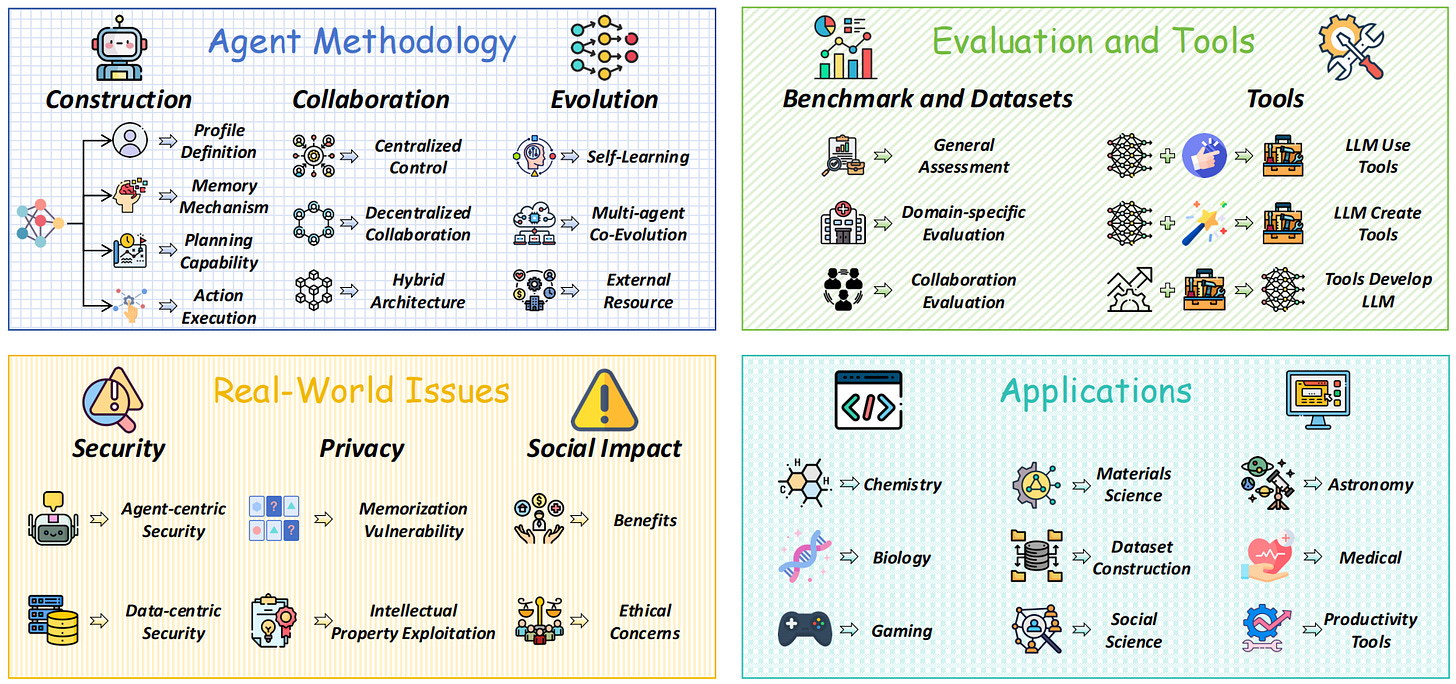
10.) Large Language Model Agent: A Survey on Methodology, Applications and Challenges( paper | repo )
The rise of intelligent agents, powered by large language models (LLMs), marks a step toward artificial general intelligence. This survey presents a taxonomy of LLM agents, exploring their architecture, collaboration, evolution, and emergent behaviors in complex environments. It unifies fragmented research, examines evaluation methods, tools, challenges, and applications, and highlights future research directions.
AIGC News of the week
1.) deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3-0324 ( huggingface )
2.) bytedance’s MegaTTS 3 ( repo )
3.) OpenAI Agents SDK support MCP ( link )
4.) Gemini 2.5: Google’s most intelligent AI model ( link )
5.) VGGT: Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer ( repo )
more AI News: live.aigc.news